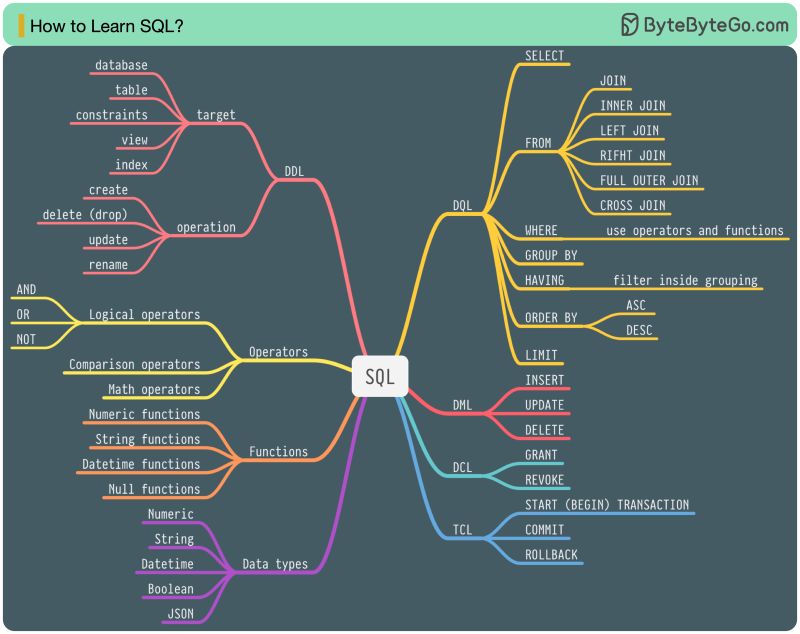
In 1986, SQL (Structured Query Language) became a standard. Over the next 40 years, it became the dominant language for relational database management systems. Reading the latest standard (ANSI SQL 2016) can be time-consuming. How can I learn it?
There are 5 components of the SQL language:
– DDL: data definition language, such as CREATE, ALTER, DROP
– DQL: data query language, such as SELECT
– DML: data manipulation language, such as INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
– DCL: data control language, such as GRANT, REVOKE
– TCL: transaction control language, such as COMMIT, ROLLBACK
For a backend engineer, you may need to know most of it. As a data analyst, you may need to have a good understanding of DQL. Select the topics that are most relevant to you.
Free EBOOK:
Enhance your SQL query writing skills to provide greater business value using advanced techniques such as common table expressions, window functions, and JSON
Purchase of the print or Kindle book includes a free PDF eBook
Key Features
- Examine query design and performance using query plans and indexes
- Solve business problems using advanced techniques such as common table expressions and window functions
- Use SQL in modern data platform solutions with JSON and Jupyter notebooks
Book Description
SQL has been the de facto standard when interacting with databases for decades and shows no signs of going away. Through the years, report developers or data wranglers have had to learn SQL on the fly to meet the business needs, so if you are someone who needs to write queries, SQL Query Design and Pattern Best Practices is for you.
This book will guide you through making efficient SQL queries by reducing set sizes for effective results. You’ll learn how to format your results to make them easier to consume at their destination. From there, the book will take you through solving complex business problems using more advanced techniques, such as common table expressions and window functions, and advance to uncovering issues resulting from security in the underlying dataset. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll have a foundation for building queries and be ready to shift focus to using tools, such as query plans and indexes, to optimize those queries. The book will go over the modern data estate, which includes data lakes and JSON data, and wrap up with a brief on how to use Jupyter notebooks in your SQL journey.
By the end of this SQL book, you’ll be able to make efficient SQL queries that will improve your report writing and the overall SQL experience.
What you will learn
- Build efficient queries by reducing the data being returned
- Manipulate your data and format it for easier consumption
- Form common table expressions and window functions to solve complex business issues
- Understand the impact of SQL security on your results
- Understand and use query plans to optimize your queries
- Understand the impact of indexes on your query performance and design
- Work with data lake data and JSON in SQL queries
- Organize your queries using Jupyter notebooks
Who this book is for
This book is for SQL developers, data analysts, report writers, data scientists, and other data gatherers looking to expand their skills for complex querying as well as for building more efficient and performant queries.
For those new to SQL, this book can help you accelerate your learning and keep you from making common mistakes.
Table of Contents
- Reducing Rows and Columns in Your Result Sets
- Efficiently Aggregating Data in Your Results
- Formatting Your Results for Easier Consumption
- Manipulating Your Data Results Using Conditional SQL
- Using Common Table Expressions
- Analyze Your Data Using Window Functions
- Reshaping Your Data with Advanced Techniques
- Impact of SQL Security on Query Results
- Understanding Query Plans
- Understanding the Impact of Indexes on Your Query Design
- Handling JSON Data in SQL Server
- Integrating File Data and Data Lake Content with SQL
- Organizing and Sharing Your Queries with Jupyter Notebooks
- Appendix – Preparing Your Environment