The diagram below shows the process. Note that the architectures for different databases are different, the diagram demonstrates some common designs.
Step 1 – A SQL statement is sent to the database via a transport layer protocol (e.g.TCP).
Step 3 – The query tree is sent to the optimizer. The optimizer creates an execution plan.
Step 4 – The execution plan is sent to the executor. The executor retrieves data from the execution.
Step 5 – Access methods provide the data fetching logic required for execution, retrieving data from the storage engine.
Step 6 – Access methods decide whether the SQL statement is read-only. If the query is read-only (SELECT statement), it is passed to the buffer manager for further processing. The buffer manager looks for the data in the cache or data files.
Step 7 – If the statement is an UPDATE or INSERT, it is passed to the transaction manager for further processing.
Step 8 – During a transaction, the data is in lock mode. This is guaranteed by the lock manager. It also ensures the transaction’s ACID properties.


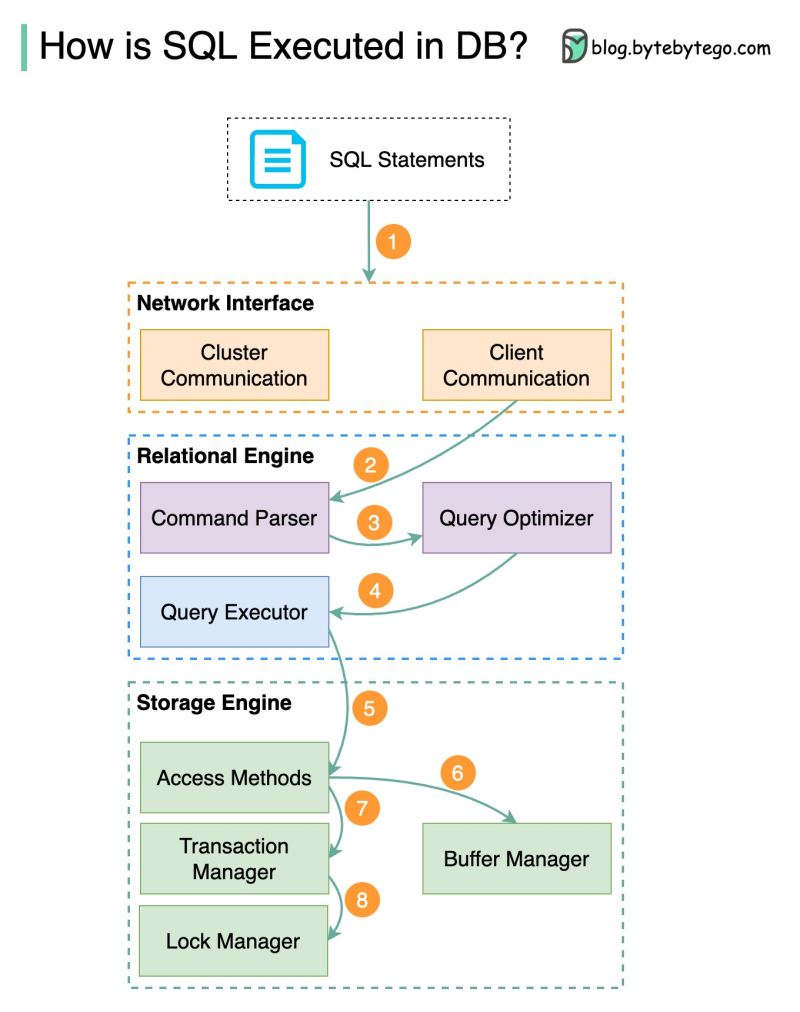
Step 2 – The SQL statement is sent to the command parser, where it goes through syntactic and semantic analysis, and a query tree is generated afterward.